Полікозанол
По́лікозано́л — загальний термін, яким позначається природна суміш жирних спиртів, котра є натуральним екстрактом рослинного воску. Використовують як харчові добавки для зниження холестерину низької щільності (ХНЩ) і підвищення ліпопротеїнів високої щільності (ЛПВЩ), а також для запобігання атеросклерозу.
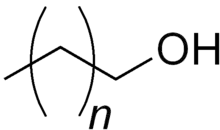 | |
| Систематична назва (IUPAC) | |
| Octacosanol, triacontanol, etc. | |
| Ідентифікатори | |
| Номер CAS | |
| Код ATC | C10 |
| PubChem | ? |
| Хімічні дані | |
| Формула | CH3-(CH2)n-CH2OH n=24-34 |
| Мол. маса | (варіює) |
| Фармакокінетичні дані | |
| Біодоступність | ? |
| Метаболізм | ? |
| Період напіврозпаду | ? |
| Виділення | ? |
| Терапевтичні застереження | |
| Кат. вагітності |
? |
| Лег. статус | |
| Використання | ? |
Фізичні властивості
Полікозанол являє собою суміш декількох жирних спиртів, отриманих з бджолиного воску, а також з воску таких рослин, як цукрова тростина[1] та ямс. У полікозанолі найбільше спирту октакозанолу (олія зародків пшениці)[2]. За ним за відсотковим вмістом йде тріаконтанол. У набагато більш низькій концентрації в полікозанолі міститься ряд інших жирних спиртів: бегеніловий спирт, лігноцеріловий спирт (CH3(CH2)23OH), церіловий спирт (C26H53OH), 1-гептакозанол, 1-нонакозанол, 1-дотріакозанол та тетратріаконтанол.
Механізм дії
- Гіполіпідемічний ефект досягається за рахунок пригнічення синтезу холестерину в момент між утворенням ацетату і мевалонату та стимуляції розпаду холестерину ЛПНЩ у гепатоцитах шляхом активації ліпаз.[3][4][5][6]
- Вазопротекторний ефект забезпечується за рахунок підвищення рівня «захисного» холестерину ЛПВЩ, перешкоджання окисленню холестерину ЛПНЩ.[4][7][8][9]
- Антитромботичний ефект досягається за рахунок запобігання агрегації тромбоцитів шляхом впливу на синтез простагландину (знижує рівень у сироватці тромбоксану A2 та підвищує рівень простацикліну) та зниження ризику тромбоутворення, не впливаючи на показники коагуляції.[4][10][11][12]
Використання у медицині
Застосовується як компонент лікарських засобів.
Торгові назви
Ноліпід, Polixar, Policosanol, Фітостатин.
Посилання
Примітки
- Marinangeli CP, Kassis AN, Jain D, Ebine N, Cunnane SC, Jones PJ (2007). Comparison of composition and absorption of sugarcane policosanols (abstract). Br. J. Nutr. 97 (2): 381–8. PMID 17298709. doi:10.1017/S0007114507336763.
- Ohta Y, Ohashi K, Matsura T, Tokunaga K, Kitagawa A, Yamada K (2008). Octacosanol attenuates disrupted hepatic reactive oxygen species metabolism associated with acute liver injury progression in rats intoxicated with carbon tetrachloride. J Clin Biochem Nutr 42 (2): 118–25. PMC 2266062. PMID 18385828. doi:10.3164/jcbn.2008017.
- Singh DK, Li L, Porter TD (2006). Policosanol inhibits cholesterol synthesis in hepatoma cells by activation of AMP-kinase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 318 (3): 1020–6. PMID 16714400. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.107144.
- I. Gouni-Berthold, H. K. Berthold, Rotenburg an der Fulda and Bonn, Germany. Policosanol: Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic signifi cance of a new lipid-lowering agent American Heart Journal, Volume 143, Number 2, 2002; 354–365.
- Menindez R., Fernandez L, Del Rio A., et al. (1994): Policosanol inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis and enhances LDL processing in cultured human fi broblasts. Biol. Res. 27:199-203.
- Menindez R., Amor A.M. Gonzilez R.M. Fraga V. and Mds R. (1996): Eff ect of policosanol on the hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis of normocholesterolcmic rats. Biol. Res. 29:253-257.
- Noa M, Mas R, Mesa R. Eff ect of policosanol on intimal thickening in rabbit cuff ed carotid artery. Int. J. Cardiol. 1998.
- Noa M, et al. Eff ect of policosanol on lipofundin-induced atherosclerotic lesions in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1995.
- Batista J., Stusser I. L., Penichet M. and Uguet E. (1995): Doppler-ultrasound pilot studyof thecff ects of long-term policosanol therapy on carotid-vertebral atherosclerosis. Curr. Ther. Res. 1995.
- Arruzazabala M. L., Valdes S., Mas R., et al. Eff ect of policosanol succesive dose increase in platelet aggregation healthy volunteers. Pharmacol. Res. 1995.
- Valdes S., Arruzazabala M.L., Carbajal D., et al. Eff ect of policosanol on platelet aggregation in healthy volunteers. Intern. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 1996.
- Carbajal D, Arruzazabala M. L., Mas R., et al. Eff ect of policosanol on platelet aggregation and serum levels of arachidonic acid metabolites in healthy volunteers. Prostaglandins Leuko. Essent. Fatty Acids 1998.
